Intramuscular vs Subcutaneous B12 Injections
Intramuscular or Subcutaneous B12 Injection?
 The most common methods for injecting Vitamin B12 and / or Vitamin C are either intramuscular or subcutaneous. Intravenous is usually done under hospital care when patients are in dire need of receiving large doses rapidly.
The most common methods for injecting Vitamin B12 and / or Vitamin C are either intramuscular or subcutaneous. Intravenous is usually done under hospital care when patients are in dire need of receiving large doses rapidly.
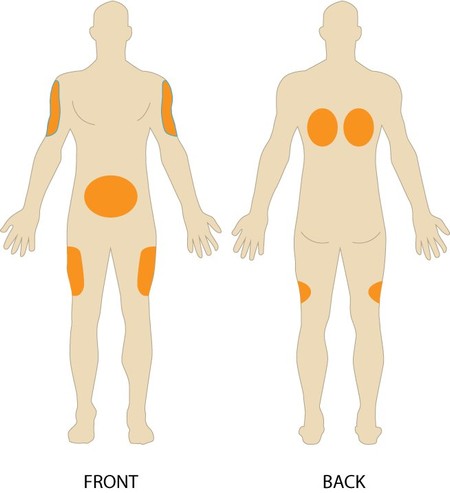
Subcutaneous injections are administered under the skin into fat between the skin and muscle. The most common injection areas are the stomach area near the belly button, front of thigh, and the side or back of upper arm.
Intramuscular injections are administered into the muscles. The most common injection areas are the gluteus, thigh, or deltoid muscles.
Which method is best for you depends on your need, comfort and who is administering the injection. Both B12 and B complex shots are given using either intramuscular or subcutaneous injections.
Both injection methods have few associated side effects and deliver effective treatment.
Looking for vitamin B injectables?
Intramuscular Injection
Advantages
This method is easy and accessible
If healthcare professionals or family is not available, you can do it yourself. Once a healthcare professional has properly trained you, an intramuscular injection is easily administered.
Intramuscular injections are touted as being easier to administer than intravenous, partly because of the easy access of the thigh muscles.
Quickly disperses medicine
Intramuscular injections quickly disperse medications into the bloodstream so that the body can rapidly disperse it where it is needed.
Large capacity for medicine
Intramuscular injections can deliver large quantities of medicine and deliver a sustained release.
How it’s done
The needle is inserted at a 90-degree angle so that it pierces the skin down into the muscle. Depending upon the location and physical body type, a 1 -1 ½ inch needle is used. B12 and B complex have a thin viscosity so a small gauge needle can be used, such as a 24-gauge needle. This thin needle does little damage to the skin upon entry.
After the needle is withdrawn, gently massage the area to begin dispersing the solution.
Disadvantages
- If the injection misses the muscle and is not deposited into fat then some or all of the medicine might be wasted. Proper training about injection locations keeps this from happening.
- Side Effects can be swelling, redness, tingling or numbness, drainage at the injection site, prolonged bleeding, and possibly some pain at the injection site. Bleeding is possible if a blood vessel is pierced.
Subcutaneous Injection
Advantages
Easy to administer
Once a person is trained, they can easily inject themselves in the stomach or thigh area.
Good absorption
Provided a patient has good circulation, complete absorption often occurs using this method. This method bypasses the oral route where medicines and supplements often are not capable of being fully absorbed and used by the body.
Not painful
Once the needle is through the skin, there are few nerve sensors, making the injection almost painless.
How it’s done
A short needle is inserted so that it pierces the skin into fatty tissue, but does not reach the muscle. Injections using a 5/8” (1.5cm) needle are inserted at a 45-degree angle. If a 1/2” (1.2cm) needle is used, the insertion is at a 90-degree angle perpendicular to the skin surface. Usually the needle size is 25 or 27 gauge.
After the needle is withdrawn, gently massage the area to begin dispersing the solution.
Disadvantages
- Smaller capacity for medicine. There is a limit to the amount of medicine that can be delivered comfortably. Medical authorities state that less than 1.5ml can be given comfortably and anything greater than 2ml causes pressure on the surrounding tissues causing pain.
- Anytime the skin is penetrated, it creates an opening for infection.
Subcutaneous Injection Sites
Once you have decided upon the method that suits you best then you can take instruction on the proper steps to insure that each of your injections are sanitary, effective and safe.
Both types of injections have few associated side effects and are very effective. However, it is suggested to consult your healthcare professional before undertaking B12 injections.